The Lean Manufacturing Principle
Efficiency is a term that plays a major role in industrial production. Lean Production means "lean production" and is an approach that
 aims to achieve the highest possible efficiency. But what exactly is behind it? What makes production lean and what exactly does Toyota have to do with it? This article answers these questions and also shows the advantages that lean production brings with it.
aims to achieve the highest possible efficiency. But what exactly is behind it? What makes production lean and what exactly does Toyota have to do with it? This article answers these questions and also shows the advantages that lean production brings with it.
Lean Production - the concept and functionality of lean production
Lean Production, also known as Lean Manufacturing, is based on the cost- and time-efficient use of production factors, including personnel, material resources and the organization of the production processes. Typical instruments of lean production, which was first discussed in an economic exchange in 1992, are teamwork, just-in-time approaches, PDCA cycles (“Plan-Do-Check-Act”) and quality management on a grand scale . The concept is based on three pillars:
1.Increasing productivity
The first module tries to reduce as many production factors as possible to a minimum. For example, throughput times are shortened, excess capacities are restricted and stocks are reduced.
 2.Quality improvement
2.Quality improvement
The second pillar deals with increasing product quality. For this purpose, regular quality controls, an ongoing review of product development and very intensive cooperation with suppliers are recommended. Find out more about the increase in quality using Kaizen or artificial intelligence via the links.
3. Increasing flexibility
In addition, great importance is attached to high flexibility. All production systems are being revised and made more flexible, and temporary capacities are being integrated into production. One of the main goals of Lean Production is to reduce waste, for example in connection with rejects, inefficient transport routes, the waiting time for certain stocks and the need for rework. The idea behind this is that such waste ultimately results in a product with an unnecessarily expensive purchase price for the customer. In short: Lean production stands for the lowest possible cost and time expenditure with the highest possible quality.
What does Lean Production have to do with Toyota?
The production system of the automobile company Toyota, TPS for short, which was changed in 1973 to more efficiency, flexibility and quality, is considered the original form of lean production. The TPS still serves as a prime example of the extremely innovative lean production at the time.
What are the advantages of the lean production strategy?
Specifically, companies that have committed themselves to the idea of lean production benefit from shorter lead times, greatly increased productivity and perfect product quality. At the same time, waste is reduced to a minimum and production speed increases. In the end, all of these points lead to cost savings.
5S for cleanliness and order
The 5S system is a lean manufacturing tool that improves workplace efficiency and eliminates waste. There are five steps in the system, each starting with the letter S:
- Sort
- Set in Order
- Shine
- Standardize
- Sustain
Seiri - sort
All objects, tools and notes that are no longer needed are sorted out. Seiton - order Work materials are arranged sensibly and ergonomically and, if necessary, provided with labels.
Seiton -Set In Order
Organize and identify storage for efficient use
Seiso – Cleanliness
Surfaces, floors and objects are cleaned thoroughly.
Seiketsu - standardize
The process is standardized so that the tidying up can be controlled and as quickly as possible in the future.
Shitsuke - self-discipline
The standard procedure developed is adhered to without exception. Seiri, Seiton, Seiso and Seiketsu are internalized through repetition and imprint themselves in a very natural way.
By the way: Safety is sometimes added as the sixth S, which is self-explanatory when it comes to making the workplace safe.
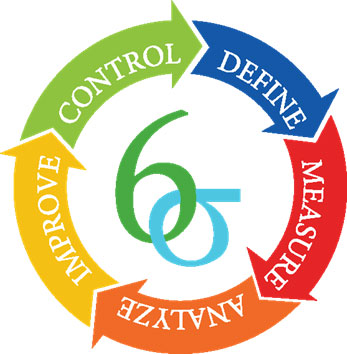 Six Sigma and Lean Production
Six Sigma and Lean Production
Six Sigma and Lean Production actually have nothing to do with each other - they are separately developed strategies. Nevertheless, they are often combined with one another and complement each other well. Six Sigma takes the statistics to their chest and uses them as a basis to optimize production processes, with the main focus on product quality and customer satisfaction. If Six Sigma is present in a production facility, this means that out of a million possible errors, only 3.4 actually happen. Therefore, the term is often used as a synonym for zero-error tolerance. When a company tackles process optimization according to Six Sigma, it usually uses the so-called DMAIC cycle. DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control. All processes are made measurable step by step and broken down into the smallest possible sections, which are optimized taking into account the previous and subsequent steps.
By the way: The error rate for companies that have not optimized their production according to Six Sigma is usually three to four Sigma. This means that out of a million possible errors, 6210 actually occur.
Does lean production also have disadvantages?
As beneficial as lean production can be for companies, it also has some disadvantages that must be considered:
No reserves
Because stocks are always kept low, short-term faults and problems in the production process may not be able to be intercepted.
Environmental pollution
Just-in-time means that suppliers often deliver relatively small quantities of a certain inventory. As a result, the environmental impact of emissions increases.
Low variance
Lean Production provides for the narrowest possible variety of products, which is not a problem in some companies, but a major problem in others.
Therefore: Lean production? Yes, please! However, you should always proceed realistically, with the respective company striving for a healthy average. Buckling the belt too tight too quickly can have extremely counterproductive consequences.

